AMD Announces 3rd Generation EPYC Evolved to Zen 3 Core, “Milan” Improves IPC with Improved Cache Hierarchy, Supports 6ch Memory
AMD will hold a press conference from its CEO, Lisa Su, from 10:00 am on March 15th (East Coast Time, March 15th Japan time). Among them, the latest product of the CPU for servers, which the company has called the development code name "Milan" (Milan, the major city in northern Italy "Milan" in English) "3rd generation AMD EPYC processor" (AMD EPYC 7003 series , hereinafter referred to as the 3rd generation EPYC) has been announced.
3rd generation EPYC announced by AMD (Source: AMD) In the EPYC processor (first generation EPYC), we adopted the Zen core, which is overwhelmingly more efficient than conventional products, and released a CPU with up to 32 cores. Achieved the same performance as Intel products, which had been given a big difference in the past.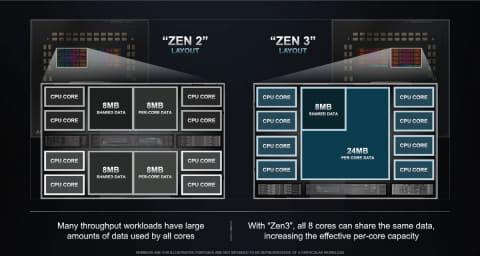
In addition, the 2nd generation AMD EPYC processor (hereinafter referred to as 2nd generation EPYC), codenamed “Rome”, announced in 2019, improved the Zen core and implemented IPC (Instruction Per Clock-cycle : The number of instructions that can be executed per clock cycle.The higher the IPC, the more efficiently the CPU can execute instructions.) It also caught up with Intel products.
In addition, the "Chiplet Architecture" that mounts multiple chips in one package, which was also used in the original EPYC, has evolved to the second generation, making it possible to dramatically increase the number of cores. 64 cores in one socket. It outperforms Intel's competitors.
In this 3rd generation EPYC, the CPU microarchitecture has evolved from the 2nd generation EPYC Zen 2 to the new generation Zen 3, and the cache hierarchy, internal branch prediction, execution units, etc. resulting in higher IPC.
The 2nd generation EPYC also supports 6-channel memory configurations, which were not supported, making it possible to consider memory configurations more flexibly.
In addition, AMD SEV-ES (Secure Encrypted Virtualization-Encrypted State), a security function for virtual machines (VMs) newly supported by the 2nd generation EPYC, has expanded from support up to conventional VMs to nesting (nesting) (Things) is also applied to VMs (VMs created within VMs), improving the security of VMs.
